NOMINAL Function in Excel to Calculate the Nominal Interest Rate
The NOMINAL function in Excel is a financial formula used to calculate the nominal annual interest rate given the effective annual interest rate and the number of compounding periods per year. The nominal rate is the stated interest rate of a loan or investment, while the effective rate is the actual rate of return or interest earned after accounting for compounding.
Syntax
=NOMINAL(effect_rate, npery)
Where:
- effect_rate:The effective annual interest rate.
- npery: The number of compounding periods per year.
The result of the NOMINAL function is the nominal annual interest rate, which is expressed as a percentage rate per year, compounded npery times.
For example
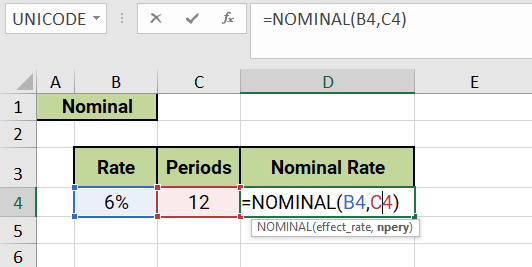
=NOMINAL(B4,C4)
The formula =NOMINAL(B4,C4) is using the NOMINAL function in Excel to calculate the nominal annual interest rate, given the effective annual interest rate and the number of compounding periods per year. Here's what each argument of the function represents:
- B4: This is the first argument of the NOMINAL function, which represents the effective annual interest rate. It is a cell reference to a cell containing the effective annual interest rate as a decimal value.
- C4:This is the second argument of the NOMINAL function, which represents the number of compounding periods per year. It is a cell reference to a cell containing the number of times the interest is compounded per year.
The result of this formula will be the nominal annual interest rate, expressed as a percentage rate per year, compounded C3 times.
For example, if cell B4 contains an effective annual interest rate of 6% and cell C4 contains the number of compounding periods per year of 12 (monthly compounding), then the formula =NOMINAL(B4,C4) will return the nominal annual interest rate, compounded monthly, as
The NOMINAL function is a useful tool for converting the effective annual interest rate into the nominal annual interest rate, taking into account the compounding periods per year. It is often used in financial analysis and investment planning to compare different financial instruments and understand their true cost or return after accounting for compounding.
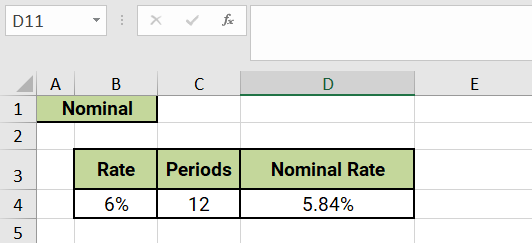
The result of this formula would be the nominal annual interest rate of 5.84%, compounded monthly.
Output
Learn All in Tamil © Designed & Developed By Tutor Joes | Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions