Understanding the PV Function in Excel for Financial Analysis and Investment Planning
The PV function in Excel (short for Present Value) is a financial formula used to calculate the current value of a series of future payments or receipts, discounted at a specified rate. It is often used in financial analysis, investment planning, and capital budgeting.The syntax for the PV function is
Syntax
=PV(rate, nper, pmt, [fv], [type])
Where:
- rate:The interest rate per period.
- nper: The total number of payment periods.
- pv:The payment made each period. This value must remain constant throughout the payment periods.
- pmt:This is the present value, or the amount of the loan. For example, if the loan is for $10,000, then the present value would be 10000.
- [fv] (optional):The future value or a cash balance that you want to have after the last payment is made. If omitted, it is assumed to be zero.
- [type] (optional): The type of payment made at the beginning or end of each period. If omitted, it is assumed to be zero (representing payments made at the end of each period).
The PMT function returns the periodic payment that needs to be made to pay off the loan. This value is negative, indicating a cash outflow or payment.
The result of the PV function is the present value of a series of future payments or receipts, discounted at the specified rate.
For example
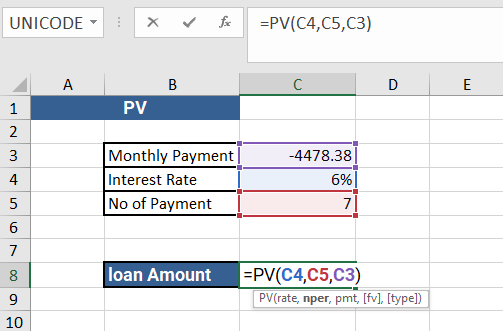
=PV(C4,C5,C3)
The formula =PV(C4,C5,C3) is using the PV function in Excel to calculate the present value of a series of future payments or receipts, discounted at a specified rate. Here's what each argument of the function represents:
- C4: This is the first argument of the PV function, which represents the interest rate per period. It is a cell reference to a cell containing the interest rate..
- C5: This is the second argument of the PV function, which represents the total number of payment periods. It is a cell reference to a cell containing the number of payment periods..
- C3: This is the third argument of the PV function, which represents the payment made each period. It is a cell reference to a cell containing the payment amount.
The result of this formula will be the present value of the series of payments, discounted at the interest rate provided, and considering the number of payment periods. It is important to note that the payment amount must remain constant throughout the payment periods.
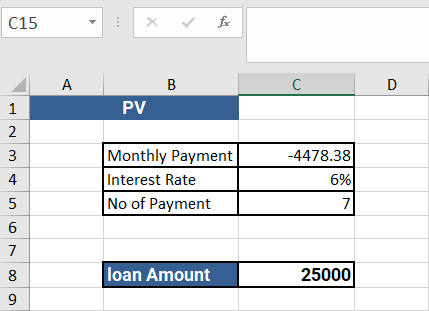
For example, if cell C4 contains an interest rate of 6%, cell C5 contains the number of payment periods of 7, and cell C3 contains the payment amount of $4478.38, then the formula =PV(C4,C5,C3) will return the present value of the series of payments, discounted at 6%, and considering the 7 payment periods.
Overall, the PV function in Excel is a powerful tool for analyzing the value of future payments or receipts, and can help you make informed financial decisions.
Output
Learn All in Tamil © Designed & Developed By Tutor Joes | Privacy Policy | Terms & Conditions